Zona de identificação
Código de referência
Título
Data(s)
- 1920 (Produção)
Nível de descrição
Dimensão e suporte
10 digital images
Zona do contexto
Nome do produtor
História biográfica
Lewis Goodbody was a son of Lewis Frederick, one of the five sons of Robert of Mountmellick, and was born at Clara in 1866 and died there at Drayton Villa on 8 January 1933, aged 66. He was educated at Birkdale, Lancashire and at Trinity College, Dublin from where he graduated in 1887. He joined the firm of Tisdall & Goodbody, later Goodbody and Tisdall, then of 15 Dame Street and Tullamore on qualifying as a solicitor in 1891. In 1893 he was active in the campaign to save the union and defeat the Gladstone home rule bill and was hon. secretary to an anti-home rule demonstration in Tullamore. Tisdall was pushed out in 1901 and the new firm of A & L Goodbody commenced in 1902. Lewis Goodbody was a keen sportsman with a strong interest in cricket and motoring. He was an original member of the Irish Automobile Club and his firm were the solicitors to the Irish Dunlop Company’s stock exchange prospectus in 1899. Goodbody lived in Kilcoursey, Clara throughout his life and what with inherited wealth and business acumen his establishment was able to support a governess, a cook and a parlour maid. Lewis Goodbody died at Clara at the age of 66 and was buried at the Friends Burial Ground, Clara. He was survived by his wife, Edith Lisetta Pim and two daughters and one son. The latter spent much of his time in India and died there in 1974.
Nome do produtor
História administrativa
A. E. or Alfred Edwin Goodbody was admitted a solicitor in 1881, having secured a silver medal at the final examinations of June 1880. He soon after set up on his own account at 15 Dame Street and later, probably in 1888 or in 1889, went into partnership with Archibald Tisdall who was based in Tullamore. He was joined in the partnership by his brother Lewis in 1891 and after this, Tisdall appears to have worked in Birr and later, after 1900, at the Dublin office. He left the partnership in 1901 and the new firm of A & L Goodbody commenced in 1902.
In 1903, the Wyndham Land Act was passed which allowed a 12 % bonus to landlords who sold entire estates to the Estates Commissioners to administer the sales under the Act. Lewis Goodbody was well placed to secure the business. He was of a Quaker family and all the other solicitors practising in Tullamore were Catholics. In 1905 Alfred sent Lewis a sum of £150, being his share of £500 secured for the sale of the Longworth-Dames estate to the Congested Districts Board. The other £200 he was holding to advance on mortgage to a client whom he was mindful of retaining. He seems to have been getting 1% on such sales but was able to quote to landlords the then Law Society scale of 2.5% and bargain thereafter. In the case of Lord Digby’s 30,000 acre estate in King’s County the firm was probably in for £3,000 fees if the matter proceeded on a total sale value of £300,000. Digby was looking for 0.75% and Lewis 1.25%. Digby had made enquiries from other landlords but so had Alfred suggesting that he would have remained firm on the 1% as is clear from a letter Alfred wrote to his brother in February 1908. With the end of the ‘big money’ estate sales, the war and the downturn thereafter inevitably the Tullamore office would have been less profitable. By this time the Dublin office was expanding and had taken in new solicitors such as G. A. Overend who was a partner in the firm by 1913 and probably commenced practice there on qualifying in 1907.
Kenneth A. Kennedy joined the firm after the death of Alfred in 1924 and was probably a partner in the Tullamore office by 1930. Kennedy was called to the bar in 1917 and qualified as a solicitor in 1924. In 1930 Kenneth Kennedy, Lewis Goodbody and G. A. Overend acquired the fee simple as joint tenants of the office premises at High Street, Tullamore held on lease since 1913. Lewis Goodbody died in 1933 and the ownership of the firm (at least as far as Tullamore was concerned) was shared between G. O. Overend and Kenneth A. Kennedy, but not necessarily in equal shares. In 1947 a new partnership arrangement was entered into between Overend and Kennedy and the following year Kenneth A. Kennedy acquired the entire interest in the building at High Street for £800. The A & L Goodbody partnership in the Tullamore office appears at this time to have comprised of G. A. Overend, Kenneth A. Kennedy and G. G. Overend. The Tullamore building was to serve the Tullamore firm, known since the late 1940s as Goodbody & Kennedy, until 1989 when the business was sold to Dermot Scanlon by Kenneth C. P. Kennedy. Kenneth A. Kennedy had remained a partner in A & L Goodbody, Dublin until his death in December 1974 at the age of 80 but the Dublin office had no involvement in the Tullamore firm probably from the late 1940s.
Nome do produtor
História biográfica
Born in 1846, the eldest son of 9th Lord Digby, he was educated at Harrow and then joined the Coldstream Guards, where he made his career, rising to the rank of Colonel and serving in the Sudan from 1885 to 1889. He also served as M.P. for Dorset from 1876-1885. On the death of his father in 1889, he resigned his commission and came home to Minterne. In 1893 he married Emily Beryl, daughter of Col. the Hon. Albert Hood and they had three sons and three daughters.
He became involved in local affairs, accepting the appointment as Chairman of the Board of Herrison Hospital, Charminster and serving as a J.P. and local magistrate, Chairman of the Dorchester Agricultural Society and honorary Colonel in the Dorset Regiment. He planted the rhododendron gardens at Minterne and sponsored plant expeditions to China and the Himalayas, breeding his own varieties in his glass houses and becoming a member of the Royal Horticultural Society.
The house at Minterne suffered from damp and dry rot, and in 1906 he fulfilled his promise to his wife to build a new house. He employed the architect Leonard Stokes, who had built Post Offices and was famously difficult to get on with. However, Lord Digby’s friendly and practical approach charmed him and he produced a marvellous design for his only country house which is still comfortable to live in.
He took an active interest in his estate at Geashill, and was saddened when the Irish Land Act of 1903 resulted in the end of the link with a number of his tenants, some of whom had been on the Digby estate for generations.
Nome do produtor
História biográfica
Edward Kenelm Digby was born in 1894, the eldest son of 10th Baron Digby. After Eton and Sandhurst, he was commissioned as a 2nd Lieutenant into the 1st Battalion Coldstream Guards in 1915. He fought at the battles of Aubers Ridge and Loos in 1915 and was promoted to second-in-command at the age of 21, after his CO was killed. He took part in the battle of the Somme in 1916, when tanks were first used; 11 officers of his battalion were killed on one day in September 1916 and all the others were wounded except him. In 1917 he fought at Passchendaele and played a major role in the occupation and final defeat of Germany in 1918.
On his return home, he married Constance Pamela Bruce, daughter of 2nd Baron Aberdare in 1919 and inherited Minterne from his father when he died in 1920. He couldn’t afford to live at Minterne, so he took the post of Military Secretary to the Governor of Australia from 1920 to 1923. With his bank balance restored, he came back to Minterne, where he bred Channel Island cattle and established a thriving dairy herd. On the outbreak of war in 1939, Minterne was taken over by a naval hospital, and the family moved to Cerne Abbas. During the war, he and Lady Digby delivered the milk around Cerne Abbas.
Following in his father’s footsteps, he bred rhododendrons and azaleas, sponsored collecting expeditions abroad. He was appointed President of the Royal Show in 1949, and President of the Royal Horticultural Society in 1959. He was Lord Lieutenant of Dorset from 1952 until his death. He was appointed Gentleman at Arms 1939, and a member of the Household Body Guard in 1952, resigning on grounds of ill-health. He was made a Knight of the Garter in 1960.
He died in 1964 and was succeeded by his eldest son, Edward Henry Kenelm, 12th Baron Digby.
Entidade detentora
História do arquivo
Zona do conteúdo e estrutura
Âmbito e conteúdo
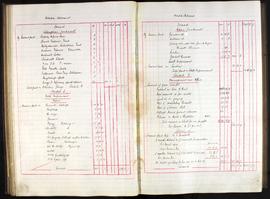
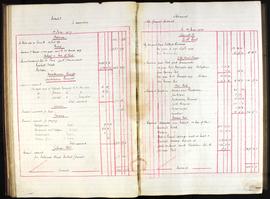
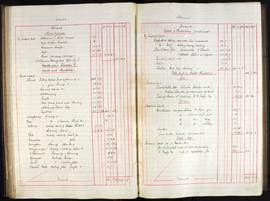
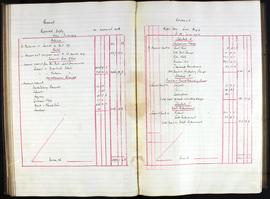
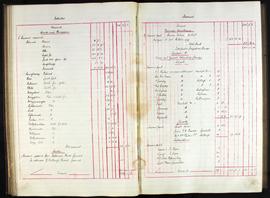
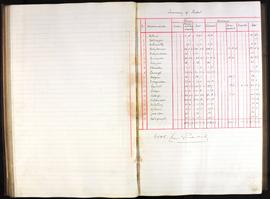
Annual report addressed to the 11th Baron Digby following the death of his predecessor. Goodbody reports that £7000 has been remitted and briefs the new Lord Digby on the state of Ireland during the War of Independence: 'Ireland continues in a disturbed and unsatisfactory condition. This neighbourhood has not escaped the general destruction of Constabulary barracks, the only three barracks on your estate having been maliciously and wantonly burnt and wrecked, those of Clonmore being wholly destroyed and of Geashill & Killeigh partially so. The police authorities having vacated them prior to their destruction have since surrendered same, with a consequent loss of future rental. Claims for compensation have been lodged for substantial amounts and are still pending.'
Avaliação, seleção e eliminação
Incorporações
Sistema de arranjo
Zona de condições de acesso e utilização
Condições de acesso
Condiçoes de reprodução
Copyright of digital images administered by Offaly County Council Heritage Office. No reproduction online, in print or broadcast without express permission of copyright holder. Original volumes in ownership of Lord Edward Digby, 12th Baron Digby.